List of Conspiracy Theories That Turned Out to Be True
Mocked. Buried. Denied.
Until the record surfaced—
and the “theory” became evidence.
Some “conspiracy theories” weren’t theories at all—just operations that stayed hidden until a memo surfaced, a hearing was forced, or a court pried the record open.
This is an evidence-first index of documented conspiracies that were later confirmed in substance by primary records (declassified files, official reports, transcripts, or admissions). If a claim can’t be anchored to the record, it doesn’t make the list.
- Each “File” is a dossier: what was alleged, what the record confirms, and what remains disputed.
- Sources are built-in: every file includes a short path of citations you can check yourself.
- Skim fast, dive deep: use the index below to jump straight to the case you came for.
Note: “True” here means the core mechanism was real (not every rumor, detail, or exaggeration attached to it).
Declassified File Index (1945–2013)
Mobile tip: use your browser’s “Find on page” and search for “File 0” to jump quickly.
[File 01] Operation Paperclip (1945–1959)
Date: 1945–1959
At the end of World War II, a secret U.S. intelligence program spirited away over a thousand Nazi scientists and engineers — not to punish them, but to put them to work for America’s Cold War arsenal. Known as Operation Paperclip, the project recruited German experts in rocketry, aviation and chemical weapons, quietly whitewashing their war-crime records to bring them into U.S. research. In 1946, a classified memo to President Truman outlined an “interim exploitation” policy: up to 1,000 German and Austrian specialists would be brought to the U.S. under military custody, despite official bans on active Nazis. These scientists — including Wernher von Braun, who would later build NASA’s Saturn V rocket — were installed at American labs and bases under false histories. Only decades later did declassified State Department documents and CIA files expose the full scope of Paperclip’s “rehabilitation” of Nazi talent. The U.S. had won the Space Race in part by pardoning the sins of the Third Reich — confirming a conspiracy long suspected by skeptics of the official postwar narrative. Even today, fragments of these files remain redacted — a reminder that the truth was never meant to be seen.
How It Was Proven
Operation Paperclip’s existence was confirmed through declassified Truman-era memos, Army intelligence files and CIA FOIA releases. In 1985, the Nazi War Crimes Disclosure Act forced the release of additional records, revealing how entire SS dossiers were rewritten or erased. Today, the National Archives houses thousands of pages showing how the U.S. quietly built its Cold War advantage on secrets once buried with the Reich.
Key Sources
- U.S. State Department Memo to President Truman (1946) – A classified directive outlining plans to exploit German scientists for U.S. military research after WWII.
- National Archives – Operation Paperclip Dossiers – Official personnel files and declassified case records from the U.S. Department of Defense’s Foreign Scientist program.
Visual Evidence
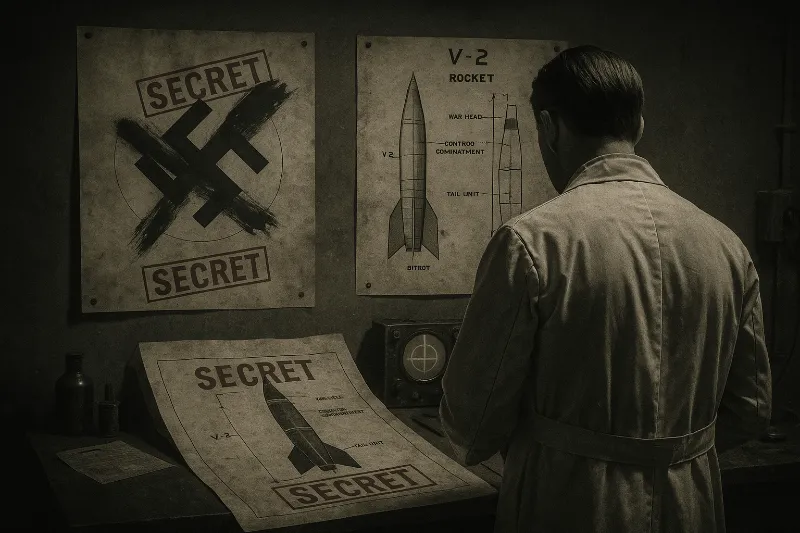


“We must secure the services of these men, regardless of their past.” — Secret Army memo, 1946
Further Reading
Deep Dive: Operation Paperclip Full Dossier
[File 02] Project MKUltra (1953–1973)
Date: 1953–1973
For decades, rumors of “government mind control” were dismissed as paranoia — until the files surfaced. The MKUltra program saw the CIA secretly dose unwitting citizens with LSD, run brutal electroshock sessions, and test mind control on hospital patients. The Church Committee in 1975 confirmed a massive covert program, and in 1977 new Senate hearings forced the CIA to admit even more. A hidden cache of over 20,000 pages survived Director Richard Helms’ purge. By 2018, newly declassified memos showed over 150 sub-projects — from brothel dosing (Operation Midnight Climax) to the infamous Subproject 68. These pages were never meant to see daylight — yet here they are.
How It Was Proven
When rumors first surfaced, the CIA denied it all. In 1973, Director Richard Helms ordered MKUltra records destroyed — but a stray box of financial files survived. In 1975, the Senate’s Church Committee forced the CIA to admit the program’s existence.
A separate Joint Hearing in 1977 unearthed new witness testimony and 20,000+ pages of surviving memos.
In 2018, the CIA declassified even more, confirming over 150 sub-projects — from LSD dosing brothels to Subproject 68’s mind control tests.
Today, every fact is backed by official FOIA files, Senate transcripts, and the Agency’s own archives.
Key Sources
- CIA Reading Room – MKUltra Collection (cia.gov)
- Senate Church Committee Report (1975) (senate.gov)
- Joint Senate Hearing (1977) (senate.gov)
- National Security Archive – MKUltra Briefing (nsarchive.gwu.edu)
Sources: cia.gov, U.S. Senate, National Security Archive
Visual Evidence
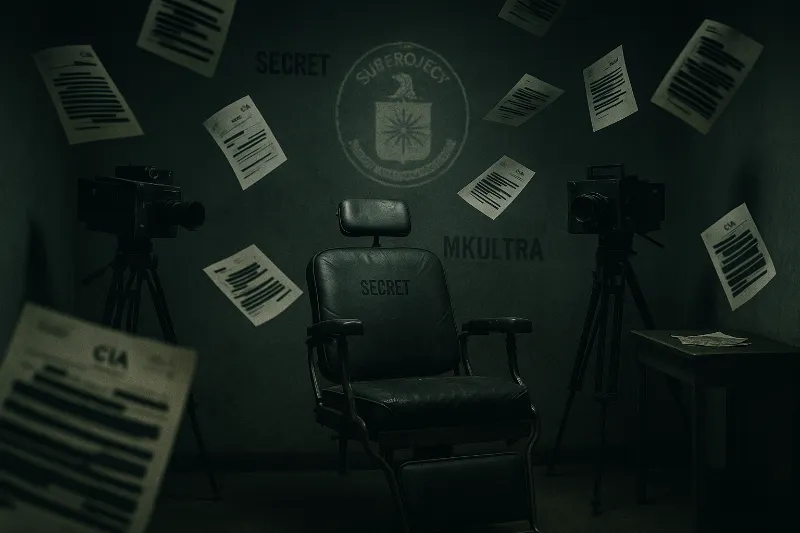


“It was necessary to conceal these activities from the American public…” — CIA internal memo, 1975
Further Reading
🔗 Deep Dive: Project MKultra
Explore leaked transcripts, subprojects and survivor testimonies:
- Project Mkultra: The Government Experiment They Tried to Bury
- Mkultra Mind Control: The Terrifying Reality Behind Mind Control
- Cia Mind Control Programs: The Terrifying Reality Behind Mind Control
Decoded in full at The Odd Signal.
🔗 Deep Dive: Coming soon.
[File 03] COINTELPRO (1956–1971)
Date: 1956–1971
In March 1971, a group of activists broke into an FBI office in Media, Pennsylvania — and leaked a trove of files exposing COINTELPRO: the Bureau’s top-secret counterintelligence program aimed at American citizens. For 15 years, the FBI conspired to “disrupt, discredit and destroy” political dissidents, targeting civil rights leaders, anti-war groups and Black liberation movements. Agents infiltrated organizations, spread fake rumors, and even tried to blackmail Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. into suicide. For years, the government denied these activities — until the stolen documents, and the U.S. Senate’s Church Committee, proved the truth. The final 1976 report confirmed that at least 50 journalists secretly worked with the CIA and FBI, and that COINTELPRO “abridged First Amendment rights” in an intolerable campaign against lawful activism. J. Edgar Hoover’s FBI truly ran a conspiracy against its own people — and only when whistleblowers forced the files into the light did Americans see how far their government went to silence dissent.
How It Was Proven
The 1971 burglary leaked over 1,000 secret files showing the Bureau’s blueprint for surveillance, infiltration and psychological warfare. The Church Committee (1975–76) hearings forced the FBI to testify under oath, confirming “Preventive Action” tactics: forging letters, planting spies, instigating internal conflicts and smearing leaders like MLK Jr. Today, the original COINTELPRO files remain in the FBI Vault, a permanent archive of domestic covert warfare.
Key Sources
- FBI Vault: COINTELPRO Files (fbi.gov)
- Britannica – COINTELPRO Overview (britannica.com)
Visual Evidence

“Disrupt, discredit and destroy…” — FBI Directive, 1968
Further Reading
Deep Dive: COINTELPRO Full Dossier (coming soon)
[File 04] Tuskegee Syphilis Experiment (1932–1972)
Date: 1932–1972
For 40 years, the U.S. Public Health Service orchestrated one of the most horrifying medical conspiracies in American history. In Tuskegee, Alabama, hundreds of Black sharecroppers were told they were receiving free healthcare — but they were actually enrolled in a secret study to observe the untreated progression of syphilis. Even after penicillin became the known cure in 1947, doctors deliberately withheld treatment. Men went blind. Lost their minds. Died. The researchers watched it all — and called it science.
Officially known as the “Tuskegee Study of Untreated Syphilis in the Negro Male,” the experiment ran without informed consent. No one told the men they had syphilis. No one told them they were test subjects. For decades, whispers of the experiment were dismissed as paranoid fiction — until a 1972 Associated Press leak forced the truth into daylight. A year later, a Senate hearing declared the study “ethically unjustified.” In 1974, survivors were awarded a $10 million settlement, and the story was finally added to America’s public health record… but only after hundreds had suffered needlessly in silence.
How It Was Proven
The conspiracy unraveled after whistleblower Peter Buxtun leaked the story to the press in 1972. The AP exposé triggered national outrage, followed by Senate hearings in 1973. The government formally ended the study, admitted wrongdoing, and settled with victims in 1974. Declassified CDC documents and medical journals now confirm what was long denied: the U.S. knowingly allowed men to die untreated for data.
Key Sources
- CDC Timeline of the Tuskegee Syphilis Study (cdc.gov)
- Britannica – Tuskegee Syphilis Study Overview (britannica.com)
- Academic review on legacy and ethics of the study (ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)
Visual Evidence
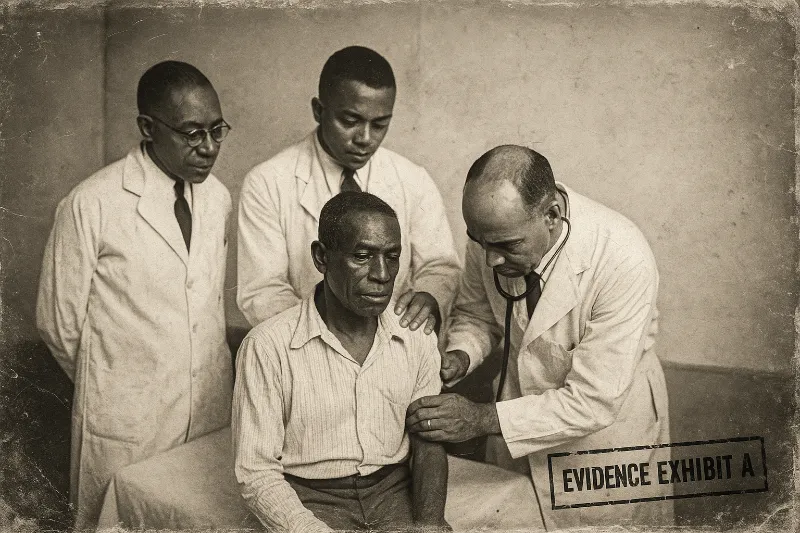

“It was ethically unjustified to withhold treatment… even after penicillin was available.” — Senate Hearing, 1973
Further Reading
Deep Dive: Tuskegee Experiment Archives (coming soon)
[File 05] Operation Northwoods (1962)
Date: 1962
It sounds like fiction: U.S. military leaders conspiring to stage terror attacks on American soil to justify war against Cuba. But in 1997, declassified Pentagon documents confirmed the existence of Operation Northwoods — a Cold War plan so shocking it was once dismissed as tinfoil-hat fantasy.
Proposed by the Joint Chiefs of Staff and presented to President Kennedy’s administration in March 1962, the operation called for faked hijackings, false-flag bombings, and even staged U.S. military casualties. One memo coldly suggested: “We could blow up a U.S. ship in Guantánamo Bay and blame Cuba… casualty lists in U.S. newspapers would cause a helpful wave of indignation.” All of it, meticulously detailed, and aimed at manufacturing consent for a full-scale invasion.
Thankfully, the proposal was rejected and never executed. But for decades, the plan’s existence remained buried — until NSA historian James Bamford uncovered it and the National Security Archive published the documents. Northwoods remains one of the clearest examples of how close the U.S. military came to deceiving its own people — not in theory, but in writing.
How It Was Proven
The full memo titled “Justification for U.S. Military Intervention in Cuba” was declassified in 1997 and made public by the National Security Archive. NSA historian James Bamford was the first to bring widespread attention to the plan in his book Body of Secrets. The unredacted documents list specific operations involving fabricated attacks, plane sabotage, and staged funerals. The fact that such plans were approved by top generals gives a chilling glimpse into Cold War logic — and the lengths to which governments may go to shape public opinion.
Key Sources
- National Security Archive – Operation Northwoods Files (gwu.edu)
- ABC News – U.S. Military Planned Fake Terror (abcnews.go.com)
Visual Evidence
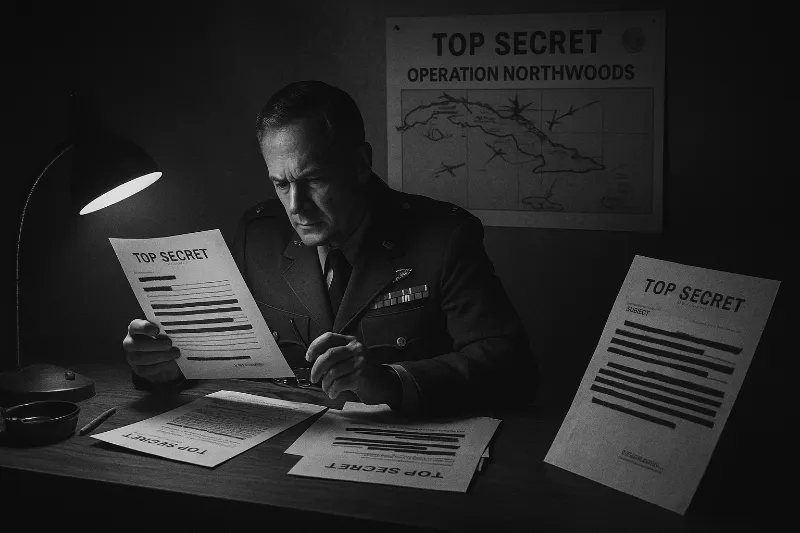


“Casualty lists in U.S. newspapers would cause a helpful wave of indignation.” — Northwoods Memo, 1962
Further Reading
Deep Dive: Operation Northwoods Documents
[File 06] Operation Mockingbird (1950s–1970s)
Date: 1950s–1970s
For decades, it was dismissed as paranoia: the idea that the CIA had infiltrated newsrooms, manipulating what Americans read, saw, and believed. But in 1975, the Church Committee confirmed what whistleblowers and dissidents had long suspected. Under the codename “Operation Mockingbird” — now widely used to describe the program — the CIA systematically recruited journalists and used the media as a covert weapon in the Cold War.
The Senate report revealed the Agency had “cultivated relationships with private institutions, including the press,” and maintained covert ties with more than 50 journalists. But it didn’t stop there. In 1977, Pulitzer-winning reporter Carl Bernstein exposed an even deeper truth: up to 400 journalists had collaborated with the CIA since the 1950s, including high-profile figures from The New York Times, Time, and CBS.
Some knowingly filed reports shaped by the Agency. Others carried out covert missions under the cover of journalism. And in at least one case, CIA memos — later unearthed in the declassified Family Jewels files — documented a secret wiretap against Washington columnists. The operation may not have always used the “Mockingbird” codename internally, but the evidence is irrefutable: the CIA ran a shadow newsroom, quietly steering narratives and exploiting the trust placed in the Fourth Estate.
How It Was Proven
The 1975–76 U.S. Senate Church Committee report directly exposed the CIA’s media operations, detailing the extent of its manipulation of journalists and media outlets. Carl Bernstein’s 1977 exposé in Rolling Stone independently corroborated the program with insider sources and interviews. Later, the CIA’s declassified “Family Jewels” documents confirmed wiretapping activities under Project Mockingbird — providing the hard paper trail once deemed impossible.
Key Sources
- U.S. Senate Report: Final Report of the Select Committee to Study Governmental Operations with Respect to Intelligence Activities (Church Committee) – Book I, Chapter 17 (1976)
— Senate investigation revealing CIA relationships with journalists and media outlets during the Cold War. - CIA Declassified “Project MOCKINGBIRD” Internal Document (2020) — A 2020‑released CIA memo detailing the 1962–63 wiretapping of two journalists under “Project MOCKINGBIRD,” found in the Family Jewels archive.
- Reporters Committee for Freedom of the Press – “CIA director personally intervenes in press wiretapping matter” — Explains how the CIA interpreted “Family Jewels” as including a press‑wiretap operation, with historical context and declassified FOIA case.
Visual Evidence

“The CIA maintains a network of several hundred foreign individuals… including journalists.” — Church Committee Report, 1976
Further Reading
Deep Dive: CIA & The Media Files (coming soon)
[File 07] Operation Gladio (1940s–1990)
Date: 1940s–1990
For decades, strange clues pointed to something hidden beneath Europe’s postwar democracies: unexplained bombings, covert caches of weapons, whispers of stay-behind militias. But it wasn’t until 1990 that the truth detonated in public. Italian Prime Minister Giulio Andreotti, under pressure from a parliamentary inquiry, admitted the existence of a clandestine NATO-backed program: Operation Gladio.
Gladio was the codename for secret “stay-behind” armies across Western Europe — guerrilla units trained and armed by NATO, the CIA, and MI6 to mount resistance in case of a Soviet invasion. But these units didn’t just wait for war. Italian investigations in the 1970s linked Gladio operatives to “strategy of tension” tactics — including false-flag terrorist attacks blamed on communists and left-wing radicals. One bombing in 1972, carried out by neo-fascists, used explosives traced back to a Gladio arms depot.
The European Parliament condemned the network, and reports surfaced of similar operations in Belgium, France, and West Germany. Though the U.S. remained evasive, former CIA Director William Colby eventually confirmed that such stay-behind programs had been funded and supported at the highest levels. For nearly half a century, a secret paramilitary web had pulsed beneath the surface of Europe — hidden in plain sight, manipulating fear to steer history.
How It Was Proven
Prime Minister Andreotti’s 1990 admission before the Italian parliament marked the beginning of Gladio’s exposure. Declassified NATO memos and investigative reports linked the network to political violence, and court trials in Italy revealed Gladio weapon stashes and names of operatives. CIA veterans, including William Colby, later admitted the existence of stay-behind operations across NATO states — confirming a long-denied shadow war.
Key Sources
- Italian Senate Disclosure on Gladio (1990) – Official confirmation by Prime Minister Giulio Andreotti before the Italian Parliament revealing the existence of NATO’s secret stay-behind army, codenamed “Gladio.”
- Declassified SIFAR Memo (1959) – ETH Zurich Archives – A military intelligence document showing Italian cooperation with NATO and the CIA to build clandestine guerrilla networks across Europe.
Visual Evidence

“Gladio was a clandestine network linked to NATO… equipped and trained to resist invasion. But it went far beyond its mandate.” — Italian Senate Report, 1990
Further Reading
Deep Dive: Operation Gladio Dossier (coming soon)
[File 08] 1953 Iran Coup – Operation Ajax (1953)
Date: 1953
For sixty years, the story lived in shadows — dismissed as Cold War paranoia or nationalist propaganda. But in 2013, the CIA finally declassified what many had long suspected: the U.S. and Britain orchestrated the 1953 coup that overthrew Iran’s democratically elected Prime Minister Mohammad Mossadegh. Codenamed Operation Ajax, the plan was executed by CIA agents working hand-in-hand with British MI6 to sabotage Iran’s sovereignty from the inside out.
The newly released files revealed everything: CIA operative Kermit Roosevelt Jr. boasting from Tehran, payments to mob leaders, and bribes to military officials. One internal memo left no ambiguity: “The military coup that overthrew Mossadegh was carried out under CIA direction as an act of U.S. foreign policy.” The objective? To stop Mossadegh’s nationalization of British-controlled oil and reinstall the Shah as a Western-friendly monarch.
Washington had long denied involvement, but the documents — telegrams, plans, receipts — tell a different story. What was once labeled a conspiracy theory became an admitted chapter in U.S. covert history. The birth of modern Iranian distrust toward the West? It began here — with a coup planned in Langley, staged in Tehran, and felt for generations.
How It Was Proven
In August 2013, the CIA publicly released its internal history of Operation Ajax. Titled The Battle for Iran, the report confirmed the agency’s direct role in the coup and revealed the full scope of its collaboration with MI6. Declassified memos, CIA cables, and British records aligned to expose the top-down orchestration of regime change, leaving no doubt about the origins of the 1953 overthrow.
Key Sources
- National Security Archive – CIA Confirms Role in 1953 Iran Coup
- The Guardian – CIA Admits Role in 1953 Iranian Coup
Visual Evidence

“The military coup… was carried out under CIA direction.” — CIA internal memo, 1953 (declassified 2013)
Further Reading
Deep Dive: 1953 Iran Coup Files (coming soon)
[File 09] Gulf of Tonkin Incident (1964)
Date: August 1964
It was the spark that ignited full-scale U.S. military involvement in Vietnam. On August 4, 1964, the Pentagon announced that North Vietnamese boats had launched a second unprovoked attack on the U.S. Navy in the Gulf of Tonkin. The very next day, Congress passed the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution — effectively giving President Johnson a blank check for war. But the second “attack”… never happened.
For years, rumors swirled that the incident had been misrepresented. Then in 2005, a declassified NSA study confirmed what skeptics had long claimed: the August 4 assault was a fabrication. Intelligence signals were misinterpreted, radar echoes misread, and — in some cases — reports were deliberately skewed to fit a predetermined narrative. NSA analysts at the time had found no clear evidence of enemy boats, but higher-ups ignored the doubts.
One internal NSA document admitted there was “an active effort to make SIGINT fit the claim” of an attack. By the time the truth emerged, 58,000 Americans and over a million Vietnamese had died in a war built, in part, on a phantom naval skirmish. The Gulf of Tonkin case is now one of the most glaring examples of manufactured consent in U.S. history — a reminder that the first casualty of war is often the truth.
How It Was Proven
In 2005, the NSA declassified a top-secret internal history authored by agency historian Robert Hanyok. The report revealed that the August 4 incident was falsely reported due to misread signals, confirmation bias, and intentional manipulation. One deputy director later admitted: “It never happened.” The lie that launched a war had been buried in signals intelligence — and eventually uncovered by the agency itself.
Key Sources
Visual Evidence

“The second attack… never happened.” — NSA Deputy Director, 2005 (declassified)
Further Reading
Deep Dive: Gulf of Tonkin Declassified Signals (coming soon)
[File 10] Prohibition Poisoning Program (1926–1933)
Date: 1926–1933
It sounds like something out of a dystopian novel: the U.S. government knowingly poisoning alcohol supplies to punish people for drinking. But that’s exactly what happened. During Prohibition, federal officials mandated that industrial alcohol — commonly stolen by bootleggers to make illicit liquor — be laced with deadly chemicals, including methyl alcohol, benzene, and cadmium. And when that wasn’t lethal enough, Treasury memos show the government decided to “double the poison content.”
Hospitals soon overflowed with victims of tainted booze. In New York alone, Christmas 1926 brought a grisly tally: 31 people dead in just a few days. Dr. Charles Norris, the city’s chief medical examiner, went public: “The United States government must be charged with the moral responsibility for these deaths.” Politicians like Senator James Reed went further, calling the policy “legalized murder.”
By the time the program ended with Prohibition’s repeal in 1933, it’s estimated that over 10,000 people had died from government-spiked alcohol. The goal was deterrence. The result was mass poisoning. What sounded like a deranged urban legend — that the feds poisoned the booze supply — was tragically and irrefutably true.
How It Was Proven
Historical investigations, including reports from National Geographic and science journalist Deborah Blum, unearthed internal Treasury Department documents from 1926–1927 that explicitly detail the plan to increase poison levels. Medical examiners’ records and contemporaneous news headlines corroborated a surge in alcohol-related deaths tied directly to the denaturing process. The “Chemist’s War,” as some called it, remains a haunting chapter of public health policy turned weapon.
Key Sources
- National Geographic – “Americans knew their booze was poisoned—and drank it anyway” A detailed article referencing contemporary medical examiner Charles Norris’s blistering indictment of the government’s poisoning policy during Prohibition
- Vox – The US government once poisoned alcohol to get people to stop drinking
Visual Evidence

“The United States government must be charged with the moral responsibility for these deaths.” — Dr. Charles Norris, NYC Medical Examiner, 1927
Further Reading
Deep Dive: Prohibition Poison Program Files (coming soon)
[File 11] Project Sunshine (1950s)
Date: 1953–1970
“If anybody knows how to do a good job of body-snatching, they will be serving their country.” That chilling quote came from Dr. Willard Libby, senior scientist at the U.S. Atomic Energy Commission, during a classified meeting in 1955. The topic: Project Sunshine — a covert operation to study nuclear fallout by collecting tissue from human cadavers, especially those of infants and children… without consent.
For years, claims of “stolen dead babies” were dismissed as macabre conspiracy lore. But declassified U.S. and British documents, and a 1995 White House investigation, confirmed the horrifying truth. Government scientists secretly harvested bones and organs from stillborn babies and deceased infants to measure strontium-90 levels from atomic testing. Grieving families were often never told. Some parents were explicitly misled while their children’s remains were dissected in the name of science.
The operation was global. British archives revealed cadaver parts shipped across the Atlantic for U.S. analysis. The most damning evidence? A transcript where Libby complains that it’s “difficult to obtain human samples,” and essentially urges his team to find ways around the law. “Our national health requires it,” he said. The program continued into the early 1970s.
How It Was Proven
The U.S. Department of Energy declassified reports in the 1990s, confirming that Project Sunshine collected tissue samples from over 1,500 deceased individuals — many infants — often through deception or without legal permission. Clinton’s Advisory Committee on Human Radiation documented systemic violations of ethics and human rights. Media exposés dubbed it the “baby body parts” scandal, and families demanded accountability. What had sounded too grotesque to believe turned out to be a state-sanctioned truth.
Key Sources
- U.S. Dept. of Energy – Human Radiation Experiments Archive
- DOE Human Radiation Experiments Roadmap – Chapter 2: Fallout Studies & Project Sunshine Official Department of Energy roadmap detailing Project Sunshine’s origins, purpose, and ethical concerns, including the collection of human tissues to measure fallout radiation.
- Advisory Committee Briefing Memo (June 9, 1995) – “Body‑Snatching” discussion Declassified memo quoting AEC Commissioner Willard Libby acknowledging the deliberate collection of infant samples—referring explicitly to “body‑snatching” for analytical purposes.
Visual Evidence

“Our national health requires it.” — Dr. Willard Libby, AEC scientist, 1955
Further Reading
Deep Dive: Project Sunshine Files (coming soon)
[File 12] Operation Snow White (1970s)
Date: 1973–1977
In what would become the largest domestic infiltration of the U.S. government in recorded history, the Church of Scientology launched a covert mission known as Operation Snow White. Far from mere legal activism, this operation planted Scientologist agents inside more than 130 government agencies, embassies, and consulates in over 30 countries — including the IRS, Department of Justice, and even Interpol.
The goal? Erase or steal any documents critical of Scientology or its founder, L. Ron Hubbard. Under the command of Mary Sue Hubbard (L. Ron’s wife), the Church’s “Guardian Office” orchestrated a global espionage campaign. Operatives posed as clerks, snuck into federal buildings after hours, wiretapped meetings, forged IDs, and smuggled out reams of classified materials.
It all unraveled in 1977, when the FBI raided Scientology offices in Washington and Los Angeles, uncovering thousands of stolen files. One agent, Gerald Wolfe, was caught sneaking into a courthouse after hours to photocopy IRS records — a mistake that led to the entire operation collapsing. By 1979, 11 top Scientologists — including Mary Sue Hubbard — were convicted of federal crimes including burglary, obstruction of justice, and theft of government property.
How It Was Proven
FBI raids exposed the operation’s breadth, and court documents detailed the inner workings of this unprecedented infiltration. Prosecutors stated: “No building, office, desk, or file was safe from their snooping.” The convictions, sentencing memos, and declassified files confirmed the conspiracy was real — a sci-fi church executing Cold War–style espionage under cover of religion.
Key Sources
- U.S. District Court Sentencing Memorandum – United States v. Mary Sue Hubbard et al. (1979) – Official court document detailing charges and judicial findings against senior Scientology operatives involved in the largest infiltration of U.S. federal agencies in history.
- FBI Vault – “Church of Scientology” FOIA File Collection – A trove of declassified FBI files on Operation Snow White, including case evidence, operational logs, and internal communications related to the Church’s covert break-ins.
Visual Evidence

“The crime committed by these defendants is of a breadth and scope previously unheard of.” — U.S. Prosecutor, 1979
Further Reading
Deep Dive: Operation Snow White Case Study (coming soon)
[File 13] NSA Mass Surveillance (2001–2013)
Date: 2001–2013 (exposed in 2013)
For decades, whispers warned that the government was monitoring every email, every call, every move. Then came the proof. In 2013, NSA contractor Edward Snowden leaked thousands of top-secret documents confirming what many dismissed as paranoia: the NSA was conducting mass, global surveillance — and Americans were not exempt.
Among the bombshells was a secret court order compelling Verizon to hand over metadata for every phone call in the U.S. daily. Other slides exposed PRISM — a program granting NSA backdoor access to tech giants like Google, Facebook, Apple, and Microsoft. Emails, chats, files — scooped without users’ knowledge. Even more chilling was XKeyscore, a tool allowing analysts to search through vast databases of online activity with minimal oversight. Your search history. Your emails. Your location. All indexed. All accessible.
Internal NSA briefings bore Orwellian slogans like “Collect It All”, and openly touted partnerships with telecoms and global internet carriers to tap directly into undersea cables and backbone networks. While officials initially denied mass spying on Americans, mounting evidence forced admissions. By 2015, a U.S. federal court ruled the bulk phone records program was illegal, confirming the critics were right.
How It Was Proven
The Snowden leaks provided direct, internal NSA documents — classified court orders, PowerPoint slides, and internal manuals — showing the scale of surveillance. The disclosures rocked the intelligence world, triggered global outrage, and led to modest reforms. But they also validated years of dismissed warnings: the haystack was real, and it was being built to find you.
Key Sources
- The Guardian – “NSA collecting phone records of millions of Americans daily” (Verizon court order) – Report with leaked FISA court order mandating Verizon to hand over daily call metadata to the NSA.
- The Guardian – “NSA Prism program taps into user data of Apple, Google and others” – Coverage of the PRISM program, revealing that the NSA had direct access to servers of major tech companies.
Visual Evidence

“Big Brother is no longer a metaphor. He’s in the server room.”
Further Reading
Deep Dive: NSA Surveillance Leaks (coming soon)
[File 14] Big Tobacco’s Health Cover‑Up (1950s–1990s)
Date: 1950s–1990s (exposed in 1990s)
For nearly half a century, cigarette companies told the world: “Smoking doesn’t cause cancer.” Internally, they knew otherwise. As early as the 1950s, scientific studies began piling up linking smoking to lung disease and death. The tobacco giants responded not with reform — but with conspiracy.
Internal memos later revealed a deliberate plan to confuse the public, intimidate scientists, and delay regulation. A 1969 document from Brown & Williamson laid it bare: “Doubt is our product since it is the best means of competing with the ‘body of fact’ that exists in the mind of the general public.” The strategy was coldly effective: fund junk science, discredit whistleblowers, manipulate the media. Meanwhile, industry research confirmed what critics were shouting — nicotine was addictive, smoking was lethal, and youth were the most lucrative target.
In 1994, seven tobacco CEOs testified before Congress under oath: “I do not believe that nicotine is addictive.” That line didn’t age well. In the following years, a trove of leaked documents — now called the Tobacco Papers — confirmed the full scope of deception. One internal R.J. Reynolds strategy memo spoke openly of securing “the young adult market,” knowing full well what that implied. The fallout culminated in the 1998 Master Settlement Agreement: $206 billion paid, secrets laid bare.
How It Was Proven
Millions of pages of litigation files, internal studies, marketing plans and court testimony revealed how the industry knowingly denied smoking’s health risks — while tailoring its products to maximize addiction. This was no misunderstanding. It was a profit-driven disinformation campaign spanning generations.
Key Sources
- “Doubt Is Our Product” Memo (Brown & Williamson, 1969) – Original internal PR playbook stating “Doubt is our product since it is the best means of competing with the ‘body of fact’…”, underpinning decades of manufactured uncertainty around smoking risks.
- UCSF Truth Tobacco Industry Documents – Massive archive (14M+ pages) of internal documents from tobacco companies, including internal strategies, research findings and marketing memos, released as part of litigation and the 1998 Master Settlement Agreement.
Visual Evidence
“A slow-motion massacre hidden behind smoke — and marketing.”
Further Reading
Deep Dive: Big Tobacco Internal Memos (coming soon)
[File 15] Dalai Lama’s CIA Funding (1960s)
Date: 1960s (declassified in 1998)
For decades, Chinese officials accused the Dalai Lama of being a covert agent in the pay of the CIA — a claim long dismissed as Communist propaganda. But in 1998, declassified U.S. intelligence documents confirmed something startling: Washington had, in fact, funded the Tibetan resistance — and the Dalai Lama personally.
Throughout the 1960s, the CIA funneled $1.7 million annually into Tibetan exile operations aimed at undermining Chinese control of Tibet. That sum included a direct $180,000 yearly stipend marked “for the Dalai Lama.” The CIA trained guerrilla fighters at a secret camp in Colorado, airdropped operatives back into the Himalayas, and coordinated psychological warfare against Beijing — all under a Cold War umbrella program signed off alongside the Bay of Pigs invasion.
Publicly, the Dalai Lama’s camp denied any CIA ties. Privately, they accepted the aid — which the Dalai Lama himself later acknowledged in his memoirs, describing it as support “against Communist aggression.” Yet as historians later pointed out, the CIA’s goals had less to do with Tibetan sovereignty and more with destabilizing China. The program was quietly shut down in the 1970s when the U.S. shifted toward diplomatic relations with Beijing.
How It Was Proven
In 1998, U.S. State Department records and CIA files were released showing the budget allocations, training missions, and internal memos confirming American sponsorship of the Tibetan resistance — including the line item for the Dalai Lama’s subsidy. It wasn’t fiction. It was fiscal reality — in a top-secret ledger.
Key Sources
- Los Angeles Times: CIA gave aid to Dalai Lama
- FRUS (Foreign Relations of the U.S.) – CIA Budget Records, 1964
Visual Evidence

“Even the icon of peace had a Cold War price tag.”
Further Reading
Deep Dive: CIA Tibetan Program Files (coming soon)
🔒 “Extra Classified Cases” (Bonus Section)
Not all conspiracies fit neatly into our Top 15. Some files stayed hidden in the archives, waiting for the right signal to bring them into the light. Here’s what we found…
[File 16] Iran-Contra Affair (1985–1987)
Date: 1985–1987 (exposed in 1986, confirmed by official investigation)
What happens when the U.S. government secretly arms its sworn enemies — and funnels the profits to fund illegal wars in Latin America? You get the Iran-Contra affair: a conspiracy so tangled, even Hollywood couldn’t invent it.
Between 1985 and 1986, officials in the Reagan administration sold weapons to Iran — a country the U.S. had officially labeled a state sponsor of terrorism — in the hope of securing the release of American hostages. The proceeds, instead of going through legal channels, were covertly redirected to support the Contra rebels in Nicaragua. Why was this a problem? Because Congress had explicitly banned U.S. aid to the Contras through the Boland Amendment.
The plot was run through a web of shadow figures, secret flights, coded bank accounts and shredded documents. When the scheme unraveled in 1986, it triggered a political firestorm. Testimonies from figures like Lt. Col. Oliver North laid bare how high-ranking officials bypassed the law, lied to Congress, and ran what was essentially a clandestine foreign policy operation from the White House basement.
How It Was Proven
The 1987 Tower Commission Report and congressional hearings confirmed the scheme in detail, supported by internal memos, arms invoices, and testimonies under oath. The Reagan administration admitted key aspects of the operation, though many claimed not to know the full extent. Several officials were indicted — and later pardoned — but the paper trail remained. A conspiracy once denied from podiums was immortalized in court records and declassified reports.
Key Sources
Visual Evidence

“They said it was about freedom. The files said it was about funds, favors, and lies.”
Further Reading
Deep Dive: Iran-Contra Archive Files (coming soon)
[File 17] Nayirah Testimony Hoax (1990)
Date: October 1990 (exposed in 1992)
In the run-up to the Gulf War, one televised plea shocked the world. A young Kuwaiti girl named Nayirah testified before Congress, claiming she had witnessed Iraqi soldiers storming a hospital and removing babies from incubators — leaving them to die on the cold floor.
The story was gut-wrenching. Politicians wept. News outlets echoed the testimony. And within weeks, public support for U.S. military intervention in Iraq soared. But there was one problem: it wasn’t true.
In 1992, investigative journalists uncovered that Nayirah was not a random witness — she was the daughter of Kuwait’s ambassador to the U.S., coached by a powerful PR firm, Hill & Knowlton, hired by the Kuwaiti government. Her statement had been carefully crafted as part of a $10-million propaganda campaign to sway American opinion. No hospital staff ever confirmed the incident. Amnesty International, which had cited the story, later retracted it. The “incubator babies” tale was pure fabrication.
How It Was Proven
Congressional records, press investigations, and internal PR memos confirmed Nayirah’s identity and the orchestration behind her testimony. The hoax was exposed in 1992 by journalists at CBC’s “The Fifth Estate” and others. It became a textbook case of wartime psychological manipulation — a conspiracy with real casualties, built on a lie.
Key Sources
- Wikipedia – Nayirah testimony – Documented summary of the false testimony given before the U.S. Congressional Human Rights Caucus, and the subsequent revelation that Nayirah was the Kuwaiti ambassador’s daughter and part of a PR campaign.
- CBC “To Sell a War” (1992) overview – Wikipedia – Description of the award‑winning The Fifth Estate documentary exposing Nayirah’s false testimony and its fabrication by Hill & Knowlton.
Visual Evidence
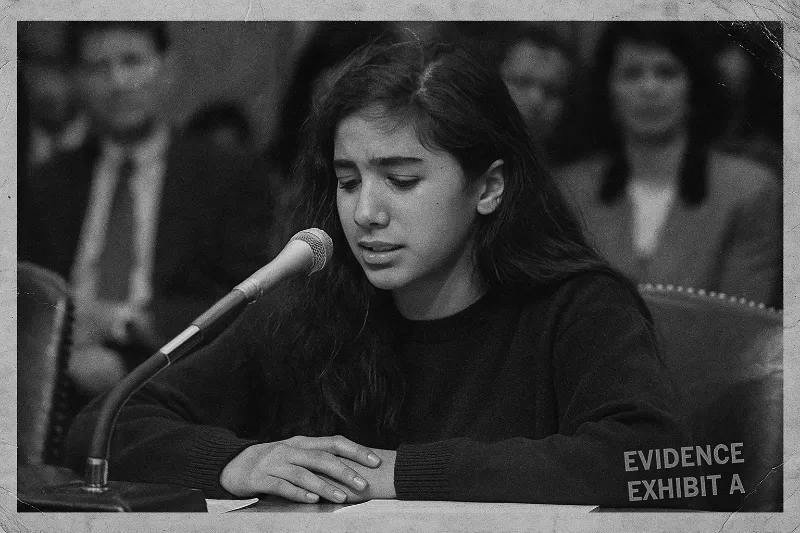

“Some lies start wars. This one nearly guaranteed it.”
Further Reading
Deep Dive: Nayirah Testimony Files (coming soon)
[File 18] The Business Plot (1933)
Date: 1933 (exposed in 1934–1935)
In the depths of the Great Depression, a bizarre conspiracy surfaced — one that sounded like political fan fiction. A group of American industrialists and bankers allegedly plotted to overthrow President Franklin D. Roosevelt and install a fascist-style dictatorship. Their choice to lead this coup? Retired Marine Corps General Smedley Butler, one of the most decorated military figures in U.S. history.
Butler didn’t play along. Instead, he went public. In sworn testimony before Congress in 1934, Butler revealed that business elites had approached him with plans to raise a private army of 500,000 veterans and march on Washington. Their goal: force Roosevelt to share power with a “Secretary of General Affairs” — effectively a corporate puppet government. Names floated in the investigation included executives from DuPont, J.P. Morgan affiliates, and major industrial lobbies.
How It Was Proven
The House McCormack–Dickstein Committee took Butler’s claims seriously. Their final report confirmed that there was indeed evidence of a plot — though no one was prosecuted. Much of the press downplayed the findings, and the names of implicated businessmen were quietly buried. But declassified archives, personal letters, and surviving committee transcripts support Butler’s story.
Key Sources
Visual Evidence
“I appeared before the committee… because I thought it was my duty as a citizen.” — Smedley Butler
Further Reading
Deep Dive: Business Plot Documents (coming soon)
Frequently Asked Questions
Final Transmission
“Some conspiracies remain theories. These 15 do not.”
Explore more: Real Conspiracies Hub · Sign up: Join The Odd Signal
These aren’t ghost stories. They’re real transmissions—once hidden by governments, corporations, and covert agencies.
Every truth exposed here is a reminder: some conspiracies are only theories until the documents surface.
And once they do… the silence breaks.
The cover is gone.
The truth is undeniable.
Explore more:
Real Conspiracies Hub

A Living Archive
This project is never complete. History is a fluid signal, often distorted by those who record it. We are constantly updating these files as new information is declassified or discovered.